Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Surface Boolean Logic
Use a surface inside a volume to set scalar values on an array in the volume.
Adopted from https://docs.pyvista.org/examples/01-filter/clipping-with-surface.html
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
Make a gridded volume
n = 51
xx = yy = zz = 1 - np.linspace(0, n, n) * 2 / (n - 1)
dataset = pv.RectilinearGrid(xx, yy, zz)
Define a surface within the volume
surface = pv.Cone(direction=(0, 0, -1), height=3.0, radius=1, resolution=50, capping=False)
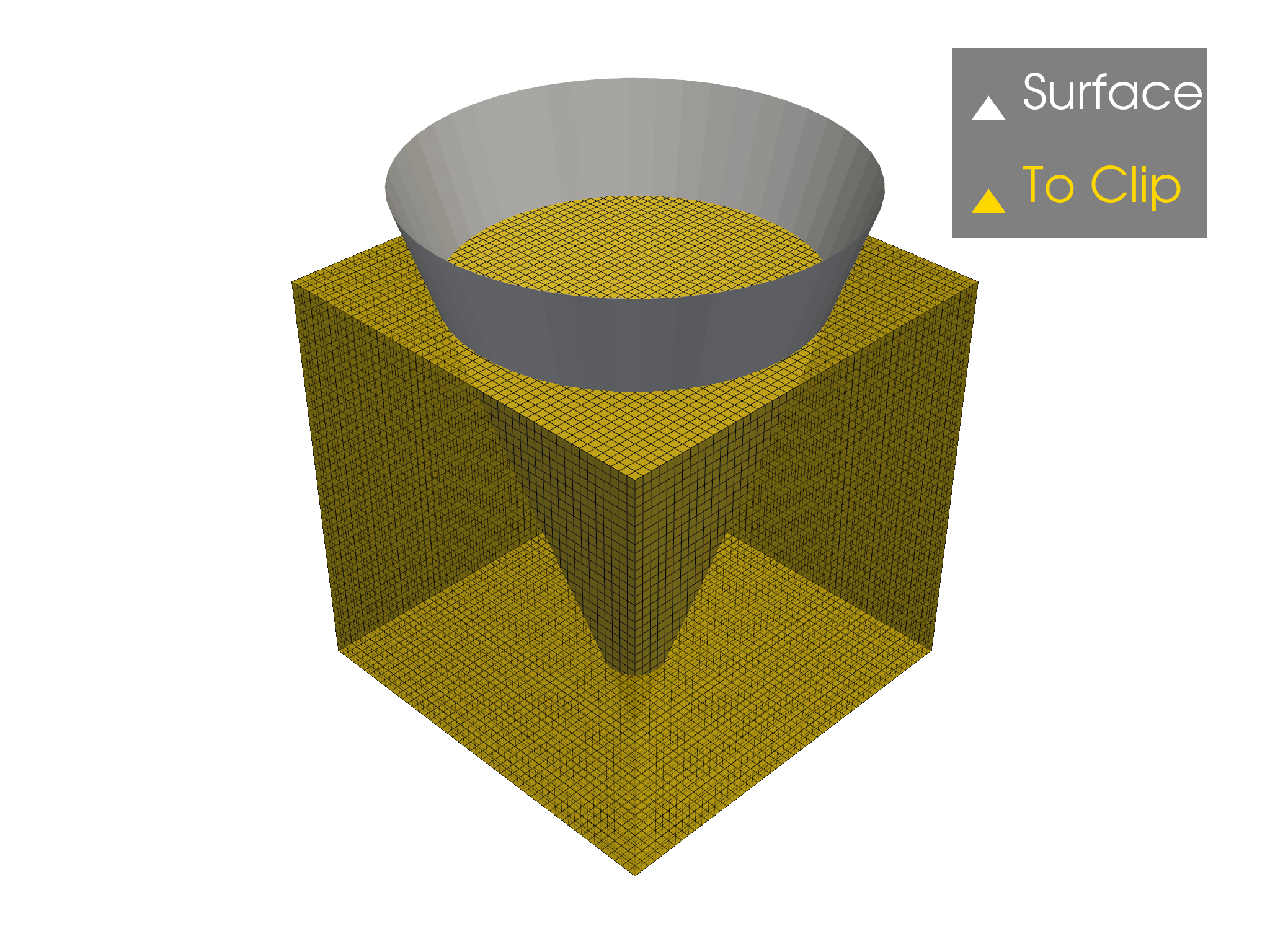
Preview the problem
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(surface, color="w", label="Surface")
p.add_mesh(dataset, color="gold", show_edges=True, opacity=0.75, label="To Clip")
p.add_legend()
p.show()
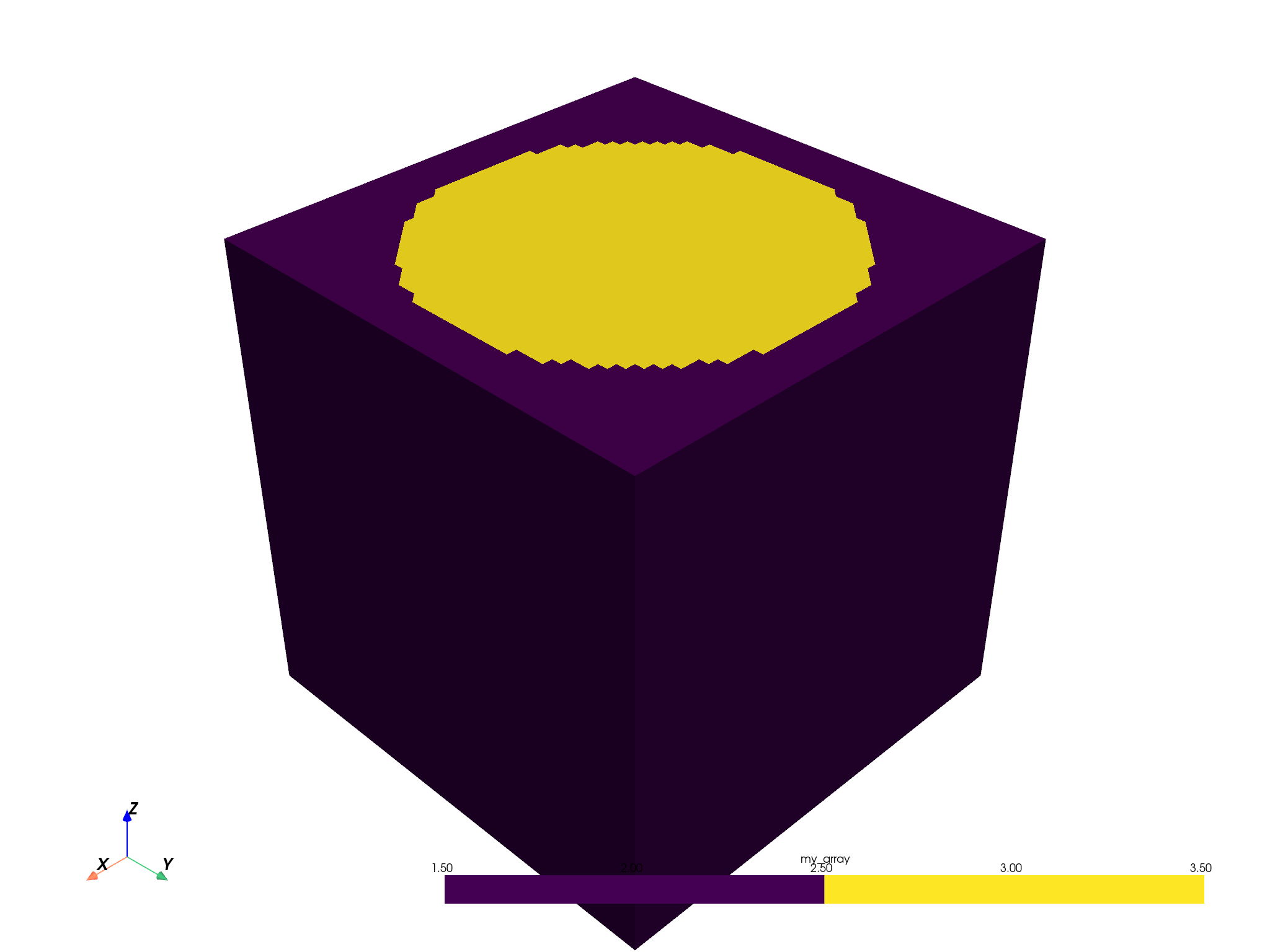
Compute an implicit distance inside the volume using this surface, then inject new data arrays
dataset.compute_implicit_distance(surface, inplace=True)
Take note of the new implicit_distance scalar array. We will use this
to fill in regions inside the surface with the value 3.0 and regions outside
the surface with the value 2.0
dataset["my_array"] = np.zeros(dataset.n_points)
dataset["my_array"][dataset["implicit_distance"] >= 0] = 2.0
dataset["my_array"][dataset["implicit_distance"] < 0] = 3.0
dataset.plot(scalars="my_array", n_colors=2, clim=[1.5, 3.5])
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.020 seconds)